Appearance
Adapter Design Pattern
Adapter is a structural design pattern that allows objects with incompatible interfaces to collaborate.
Category
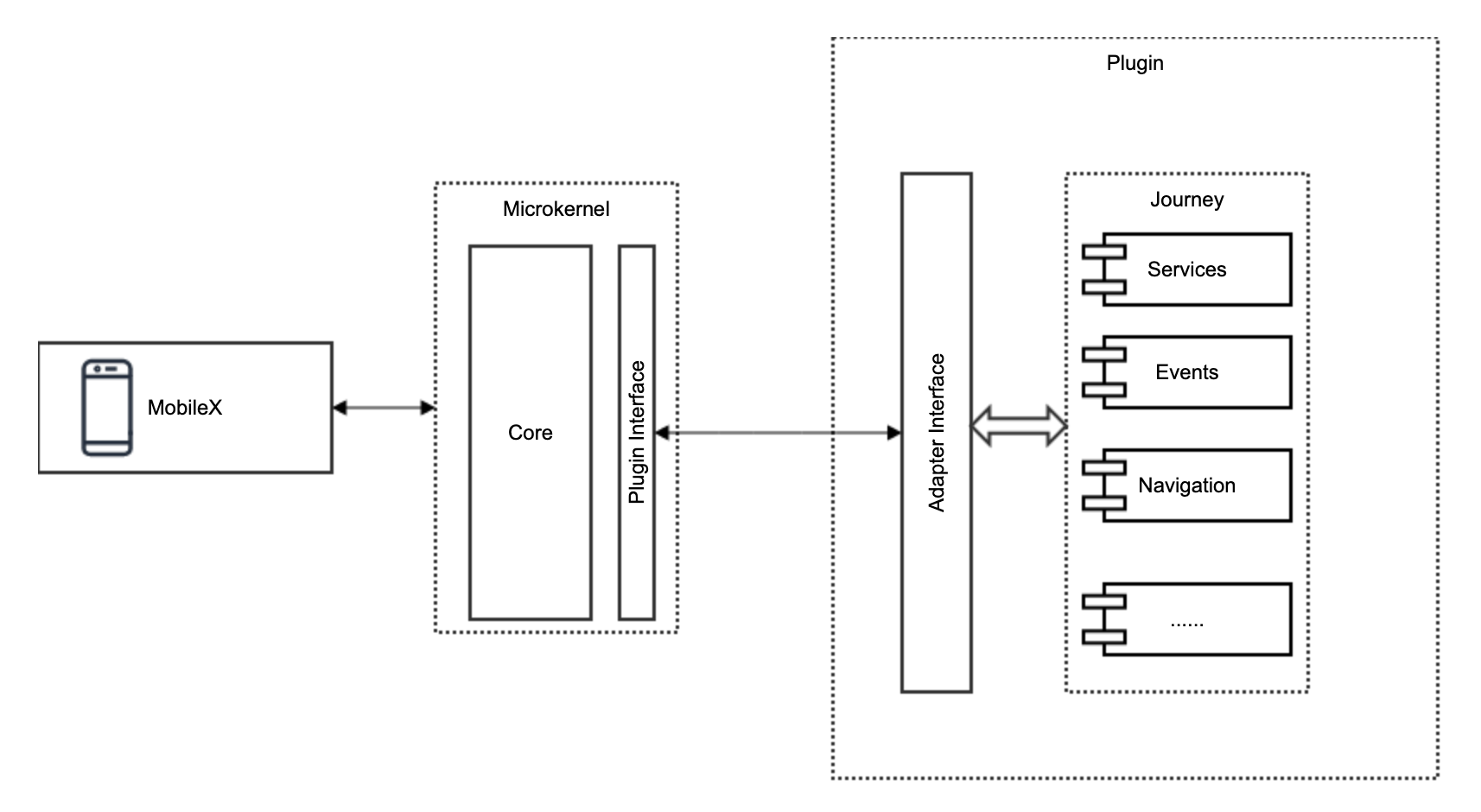
PlatformHub Integration
Scope - Problem
PlatformHub requirement is to translate legacy api communication to new ways in existing journeys or components. In this scope we have two different entities with different public interfaces: The pre-existing one and the new adapter interface that will allow the journey or component to communicate with PlatformHub.
Scope - Pattern Context
Adapter Pattern allows objects with incompatible interfaces to collaborate. The Adapter pattern lets you create a middle-layer class that serves as a translator between your code and a legacy or 3rd-party class.
When to Use This Pattern
We can use the Adapter pattern for the below cases.
- Use the Adapter class when you want to use some existing class, but its interface isn’t compatible with the rest of your code.
In MX case, as per the new simplified API contract and API calling mechanism designed for PlatformHub, the requirement is to translate the new api call to the legacy api call in the existing legacy journeys/component, hence the Adapter is useful when you have to establish an interaction between two objects with different interfaces.
Design and Implementation
High Level View
Reference Class Structure
This implementation uses the object composition principle: the adapter class i.e. (Plugin Own Interface) implements the interface of one object and wraps the other one i.e. (PlatformHub Plugin Interface). 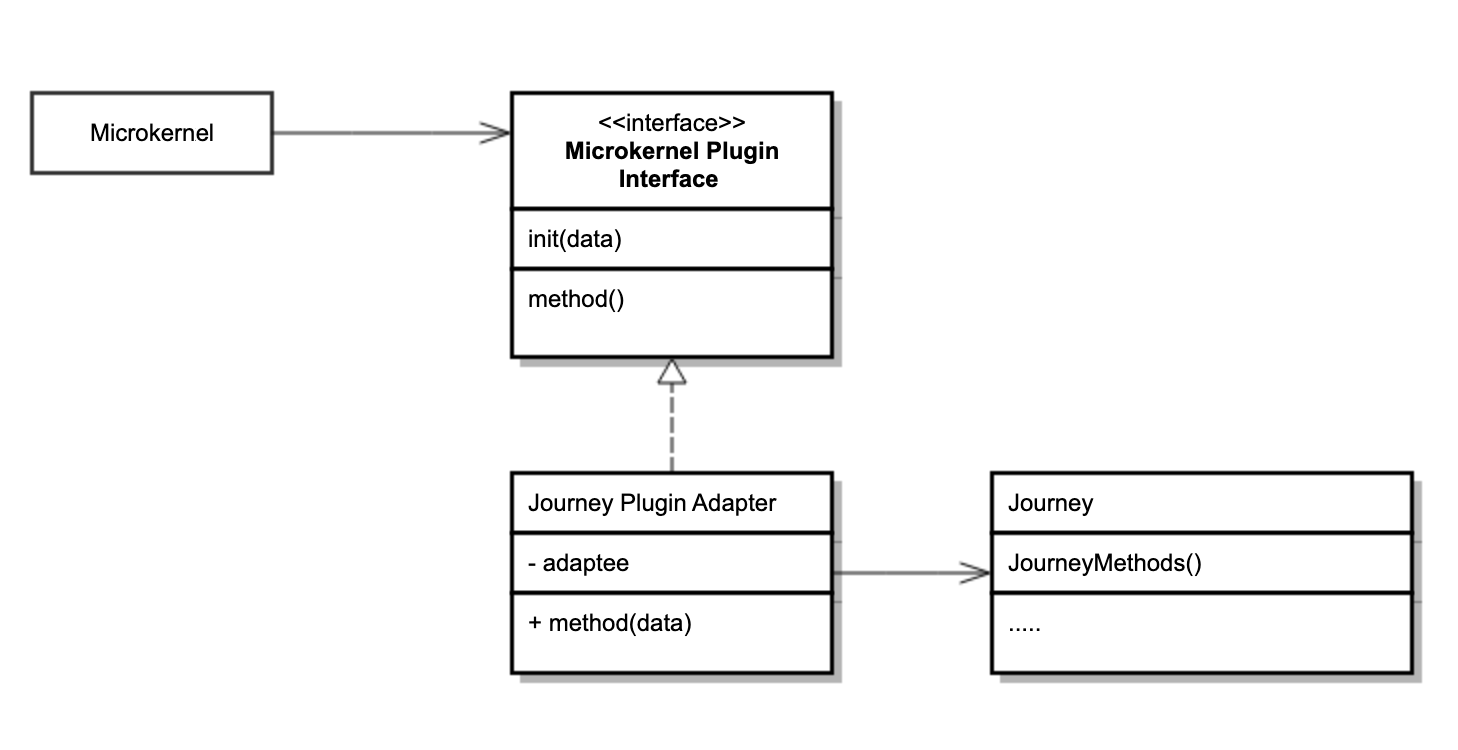
Code
PlatformHub
java
class MainApplication : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
val helloWorldPlugin = HelloWorldPlugin()
var policies = helloWorldPlugin.getPolicy()
}
}Journey Plugin Adapter
java
class HelloWorldPlugin : Plugin {
override fun init(context: Context, eventDispatcher: EventDispatcher, configFilesMap: Map<String, InputStream>) {}
override fun getPolicy() {}
override fun onEvent(event: Event) {}
override fun onEventSync(event: Event) {}
override fun onEventAsync(event: Event): Flow<JSONObject> {}
private fun configurePlugin() {}
}PlatformHub Plugin Interface
java
interface Plugin {
fun init(
context: Context,
eventDispatcher: EventDispatcher,
configFilesMap: Map<String, InputStream>
)
fun getPolicy(): Policy
fun onEvent(event: Event)
fun onEventSync(event: Event): JSONObject
fun onEventAsync(event: Event): Flow<JSONObject>
fun name(): String = getPolicy().name
}Issues and Considerations
- All requests are forwarded, so there is a slight increase in the overhead.
- Adapter refactoring would be costly.
- As adapter/plugin would be the single door for all communication so it will increase code complexity and code size so frequently need to check the Cyclomatic complexity of code.
Forces and Constraints
- Plugin Adapter should follow the Plugin protocol defined in PlatformHub.
- Any crash or issue in the adapter initialisation could stop all communication between client and respective functionalities.
- Testing would be needed as the initialisation & communication of the Adapter is at run time. Can't detect these issues at build time.
Document Reference
Read More Patterns